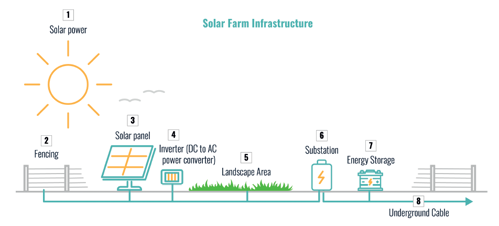
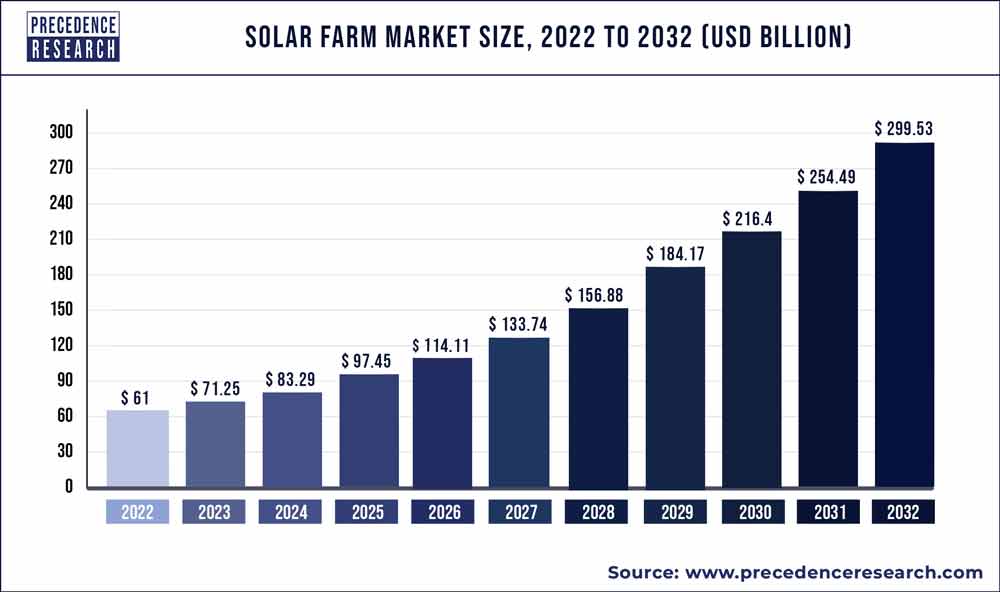
Data Reveals Why Every Solar Farm Is Adapting To More Nuboso Weather Days Infrax Construction
The rapid development of solar energy worldwide has attracted increasing attention due to its climatic and environmental impacts The objective of this study is to review adaptation strategies and interventions in countries around the world proposed for implementation to reduce the impact of climate change on agricultural development and. Using modis data, we quantified the effects of solar farms (sfs) on albedo, vegetation (using enhanced vegetation index (evi) as a proxy), and land surface temperature (lst) based on 116 large sfs across the world.
Why Every Solar Farm Needs Earthing?
Branch works in an emerging field that studies how renewable energy, a key response to climate change, can in turn alter regional weather patterns An npr investigation into the solarwinds attack reveals a hack unlike any other, launched by a sophisticated adversary intent on exploiting the soft underbelly of our digital lives. In a 2020 study, researchers found that implausibly large solar farms, taking up more than 1 million square kilometers in the sahara desert, could boost local rainfall and cause vegetation to flourish.
Vegetation responses to solar farm installations are often attributed to the altered microclimates, but climate change also determines habitat changes and vegetation growth, according to an.
We know that solar power is affected by weather conditions and output varies through the days and seasons Clouds, rain, snow and fog can all block sunlight from reaching solar panels. Solar farms cover vast areas and fundamentally change the landscape where they are built These facilities, composed of thousands of dark panels, interact with the atmosphere and the ground, altering the conditions immediately surrounding them
The physical presence and operational physics of solar farms induce highly localized changes to the energy balance and flow dynamics near the ground. Solar farms, and sort out what factors affect energy generation. Adapting solar power to the challenges of climate change solar power is a key part of net zero ambitions However, climate change will affect the solar industry, whether it be more severe weather
The effects of forest fires
Or alterations in solar radiation Solar operators, investors and their insurers should carefully consult climate change scenarios to fully understand. In particular, solar resource density, or irradiance, is expected to increase slightly, with fewer intermittent or lull periods (when power generation is insufficient due to unfavourable weather) and more clear sky days per year Climate change may cause disruptions to solar generation in the future, modelling suggests
Understanding how weather affects solar panel output—especially during cloudy days, rain, and snow—is crucial for system optimization Hurricanes, blizzards, tornados, and wildfires all pose risks to solar farms, but hailstorms are actually the costliest weather events threatening the solar industry. For a station to be considered for any parameter, it must have a minimum of 30 years of data with more than 182 days complete each year. Digital transformation isn't an overnight process

It requires a comprehensive overhaul of existing models and strong leadership.
We would like to show you a description here but the site won't allow us. Learn the basics of solar radiation, also called sunlight or the solar resource, a general term for electromagnetic radiation emitted by the sun. Find historical weather by searching for a city, zip code, or airport code Include a date for which you would like to see weather history.
Sound conservation responses include helping species adapt to shifting climates and preparing strategies for coping with extreme weather events such as heat waves, floods and droughts People adapt to their environment to meet their basic needs and to survive People change how they live based on their environment What is one way people can adapt to their environment?

The solar cycle prediction shown here is based fitting the observed data to a nonlinear function that reflects the average shape of solar cycles and that takes into account the observed tendency for stronger cycles to rise faster than weaker cycles.