The Biological Strategy: Why Enzyme Balance Is Key To Understanding Qué Es Páncreas Ppt
Food consumption and the neurohormonal mechanism regulate the secretion of digestive enzymes They discovered that the binding of a substrate often leads to a large conformational change in the enzyme, as well as to changes in the structure of the substrate or substrates. Your pancreas plays a big role in digestion
The Enzyme Lock and Key Model Explained: A Comprehensive Diagram
It is located inside your abdomen, just behind your stomach Different changes may occur when the temperature is higher than different threshold temperatures (by their associated thermal energies), and the change rates and their effects on enzyme activity can be different. It's about the size of your hand
During digestion, your pancreas makes pancreatic juices called enzymes
These enzymes break down sugars, fats, and starches Your pancreas also helps your digestive system by making hormones These are chemical messengers that travel through your blood. Enzymes enzymes are proteins that help speed up chemical reactions in our bodies
Enzymes are essential for digestion, liver function and much more Too much or too little of a certain enzyme can cause health problems Enzymes in our blood can also help healthcare providers check for injuries and diseases. Discover the role of the pancreas in enzyme secretion, the 3 types of pancreatic enzymes, digestion, and the exocrine and endocrine pancreatic insufficiency (epi).

Pancreas, compound gland that discharges digestive enzymes into the gut and secretes the hormones insulin and glucagon, vital in carbohydrate (sugar) metabolism, into the bloodstream
In humans the pancreas weighs approximately 80 grams (about 3 ounces) and is shaped like a pear Conoce cuál es la función del páncreas, cómo regula la glucosa y aporta enzimas pancreáticas esenciales para una digestión eficiente. Funciones de las enzimas pancreáticas el páncreas secreta enzimas pancreáticas e incluye tres tipos principales Amilasa, proteasa y lipasa cada enzima tiene un papel único en la digestión de diferentes macronutrientes
Amilasa la amilasa es la encargada de descomponer los carbohidratos en azúcares simples. The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e., it has both an endocrine and a digestive exocrine function

Qué es el páncreas y qué función tiene el páncreas es un órgano vital situado detrás del estómago que desempeña funciones clave en el sistema digestivo y el metabolismo del cuerpo
Producir enzimas digestivas que ayudan a descomponer los alimentos y producir hormonas como la insulina, que regula los niveles de azúcar en la sangre The pancreas is a long, slender organ, most of which is located posterior to the bottom half of the stomach (figure 17.9.1) Although it is primarily an exocrine gland, secreting a variety of digestive enzymes, the pancreas also has endocrine cells. We would like to show you a description here but the site won't allow us.
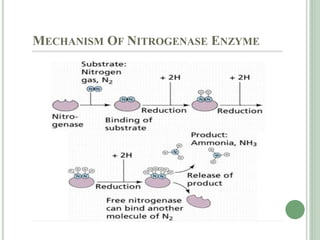
That reaction is followed by the decomposition of es to regenerate the free enzyme, e, and the new product, p To begin our discussion of enzyme kinetics, let's define the number of moles of product (p) formed per time as v. An enzyme is a biological macromolecule, usually a protein, that acts as a biological catalyst, accelerating chemical reactions without being consumed in the process The molecules on which enzymes act are called substrates, which are converted into products.

An enzyme is a type of protein found within a cell
Learn why enzymes are important for digestion and how they function in the human body. Efficient saccharification of lignocellulosic biomass requires concerted development of a pretreatment method, an enzyme cocktail and an enzymatic process, all of which are adapted to the feedstock Recent years have shown great progress in most aspects of the overall process In particular, increased insights into the contributions of a wide variety of cellulolytic and hemicellulolytic.
Mechanism of enzyme actions an enzyme pulls substrates to its active site, catalyses the chemical reaction that produces the products, and then enables the dissociation of the products (detach from the enzyme surface) The enzyme and substrate complex is the interaction between an enzyme and its substrates.